Have you spent years mastering your SEO, only to find that your well-ranked website is nowhere to be seen?
Your domain authority is high and you constantly outrank your competitors, but during a ChatGPT search for the ‘best product/service near me,’ your domain falls to the bottom of the list.
Don’t worry, it’s not a glitch, just Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO) in action.
Today, in the United States alone, more than 15 million internet users turn to AI tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude first when searching for information online.
These generative search engines are powered by user intent and are designed to provide direct, comprehensive answers in a matter of seconds.
If you’re optimising your website under an old SEO playbook, you may rank well in a search engine result, but when it comes to mastering AI overviews and LLM search responses, you’ll fall short.
Luckily, generative engine optimisation (GEO) and AI SEO go hand in hand with search engine optimisation (SEO). Stick with us as we guide you through every step of the GEO process and propel your business to the top of AI results.
The Rise of AI SEO
There’s no doubt that generative engines are on the rise. Recent data from Insidea shows that 63% of modern searchers now prefer AI assistants to traditional search engines for quick answers.
The era of scrolling through SERPs is coming to an end. Instead, today’s searchers want instant answers to their questions, delivered to them at the top of the screen.
Google responded to this in 2024 by releasing its first ‘AI overview’ feature, which delivers AI-generated summaries at the top of search results. This powerful summary box contains snippets of content from the best-fitting sources and links them as a source that users can interact with.
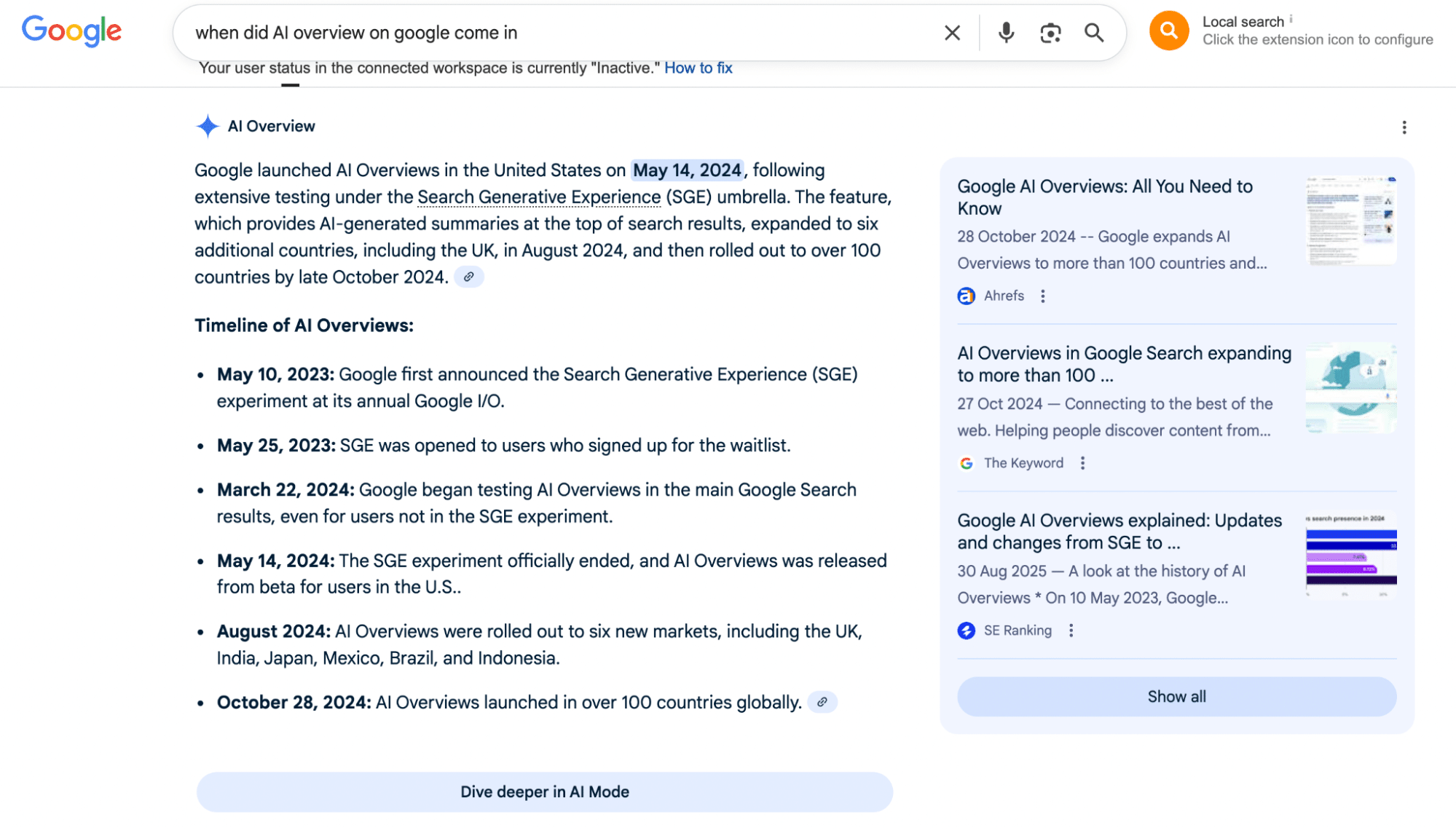
In the case of the question above, the AI overview has immediately provided all relevant information, reducing the need to scroll further or manually extract it from top-ranking blogs.
What this tells us is that, to secure a spot as a source in an AI overview, your website doesn’t have to be the highest ranking domain, but instead includes content that is formatted in a way that generative search engines can scan and reuse in a quick-fire answer.
Over 70% of AI-powered plugins and generative Google searches rely on external web content for accurate data.
If your content is up to scratch, you’ll find it much easier to perform well in a generative searchscape.
What are Generative Engines?
A generative engine is an AI-powered search engine that generates its own answers to user queries, based on data from multiple web sources.
Rather than listing links to relevant webpages, generative search engines rely on large language models (LLMs) to understand the query’s context and pull relevant information from the web to answer the question.
By providing human-like text responses, often backed by multiple linked sources, generative search engines cut out the middleman, giving users direct access to easy-to-understand information in a matter of seconds.
How Generative Engines Work:
Complex Queries: The generative search process begins when users input long, complex queries, questions or even verbal paragraphs into a generative search engine.
Initial Breakdown: Once received, a generative search engine uses AI to break a long-form prompt into smaller, more searchable queries.
Source Search: With more minor queries to answer, generative engines then retrieve data from internal training, and external web sources that naturally match the query.
Answer: Once the data is gathered, LLM features summarise the information and generate a human-like response to the initial query.
Instead of relying on a list of best-fit links, generative engines deliver the user a direct, generated answer with added citations.
Examples of Generative Engines
There are plenty of generative engines in action. After the most popular generative engine, ChatGPT, reached 100 million monthly users within just two months of its 2022 launch, many other generative search engines have followed suit.
In 2025, ChatGPT has more than 400 million weekly users and has become the fastest-growing app to reach that milestone.
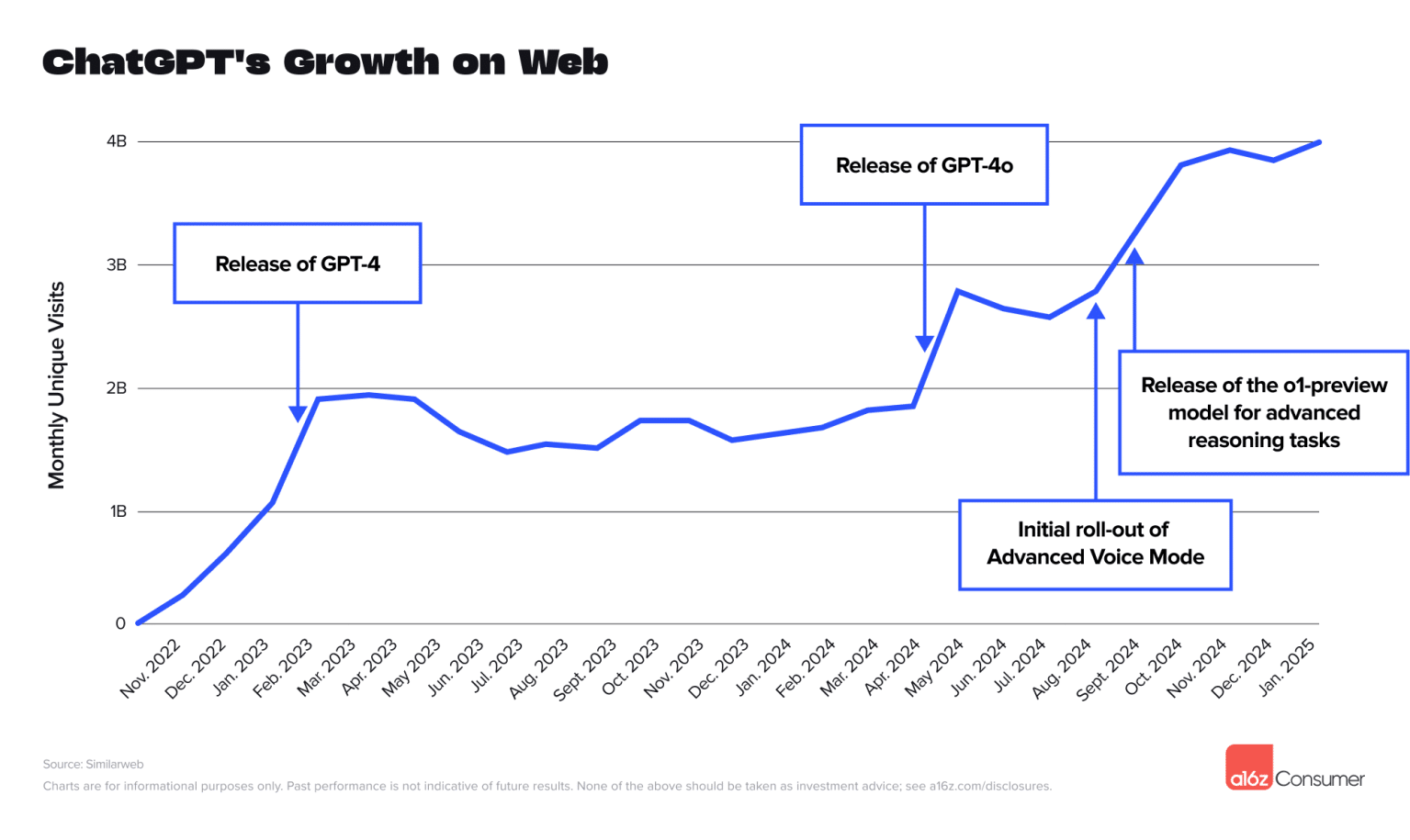
(Image Source: Tech Crunch)
Also known as OpenAI, ChatGPT is an advanced chatbot that uses an LLM called GPT to generate human-like answers to user queries.
Instead of typing questions into Google’s search bar, online searchers are now turning to generative apps like ChatGPT, which has resulted in 30,000 unique domains receiving referral traffic from OpenAI every day.
However, ChatGPT isn’t the only generative search engine making its mark:
Gemini (Google): Google’s generative partner, Gemini, works like ChatGPT, integrating with Google’s search capabilities to help users discover information and complete tasks.
Copilot (Microsoft): Microsoft has also followed suit with Copilot, an AI-powered assistant integrated with Windows and Office, designed to aid users with desktop tasks.
Claude: Similar to ChatGPT, Claude is a chatbot designed to provide recommendations and information. Drawing information from established databases and business directories, it’s the perfect partner for businesses.
Perplexity AI: Perplexity is a conversational search engine designed to provide users with direct answers to their queries, citing and synthesising sources.
The generative engine market is growing rapidly and is projected to reach $328.0 million in 2025.
As LLM models get smarter, chatbots like ChatGPT and Claude instantly become the go-to search applications for users seeking quick, direct answers to their questions.
Understanding GEO vs Traditional SEO
Generative engine optimisation (GEO) – also known as AI SEO and LLM SEO – shares many strategies with traditional search engine optimisation (SEO).
The foundations of both GEO and SEO are strong content, powerful keywords, and the ability to answer user queries.
This said, at their core, GEO and SEO have different priorities. Traditional SEO focuses on making a website rank high in traditional search engine results pages (SERPs) to drive clicks. GEO, however, targets AI search systems to ensure content is included in AI-generated answers and in Google’s AI overview.
Breaking all the rules of traditional SEO, GEO focuses less on achieving the highest domain ranking and instead prioritises user intent to boost visibility in an AI-powered search.
Businesses that combine GEO tactics with traditional SEO strategies ensure visibility across both conventional and AI-powered search surfaces.
To do this, we must first understand the differences between GEO and SEO:
GEO (Generative Engine Optimisation)
Target: Generative engine optimisation targets AI-driven search tools and generative engines such as ChatGPT and Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE). Rather than preparing your domain to rank at the top of SERPs, your goal is to get your website’s content featured in AI-generated answers and AI overviews.
Goal: Build brand recall across generative engines and drive referral traffic to your domain.
Metrics: AI answer inclusion rate, mention rate, and attribution quality. The key here is to track AI overviews for your target keyword and focus on building mentions in generative results.
Content: Well-structured, self-contained content ‘chunks’ that can be easily retrieved by AI-powered search engines. Focus on user intent, direct answering and conversational keywords.
Traditional SEO (Search Engine Optimisation)
Target: Search engine optimisation centres around traditional search engines such as Google and Bing. SEO strategies target search results pages (SERPs), with the intention of ranking first for a relevant keyword or query.
Goal: Rank highly in a search result and encourage users to interact with your domain.
Metrics: Domain authority, click-through rate (CTR), bounce rate and conversion rate.
SEO success is measured in several ways. The most common metric is Domain Authority, a third-party domain score that indicates how authoritative your website is in Google search results. Anything between 50 and 100 suggests that your content is a credible source, worthy of a notable ranking in a SERP.
On-page metrics such as CTR and bounce rate help measure how many users interact with your content as a direct result of your SERP ranking position.
Content: Long-form resources such as blogs, articles and published data that search engine crawlers can index.
Why Both are Important
GEO and SEO go hand in hand. Generative engine optimisation helps your brand build visibility in an AI search space. If your content is constantly featured in AI overviews, you instantly build awareness and domain authority.
As you build visibility in multiple search spaces, your credibility as a powerful source also impacts your SEO, leading to higher rankings and more referral traffic to boost on-page metrics.
If you optimise for both GEO and SEO, you build a stronger domain, which is crucial in such a competitive search landscape.
Why AI SEO Matters Now
AI optimisation (or LLM optimisation) now matters more than ever before. While traditional SEO is still extremely important, optimising your content for large language models could propel your website into new search territory in an AI-driven era of online search.
It’s no secret that AI overviews are becoming more common in general Google searches. Studies suggest that organic web traffic from traditional searches is declining by 15-25%, and that more than 80% of searchers now rely on AI-generated results for at least 40% of their searches.
New research from Semrush also suggests that LLM traffic will overtake traditional Google search by the end of 2027, with the most recent data revealing that there has been an 800% year-on-year increase in LLM referrals since 2022.
While search success used to be attributed to securing the first position on SERPs, today a ‘search victory’ looks very different.
As we step into an era where SERP results are condensed into a direct AI-overview box or a ChatGPT response, in the future, there may not even be a ‘top spot’ for domains to play for; instead, it’ll be a battle for a feature as a top recommendation in a generative engine result.
The Core Principles of Generative Engine Optimisation
Before we jump into the list of ways to improve your generative engine optimisation, let’s first take a look at some of the core principles and key concepts that will help guide your GEO strategy:
User Intent
When mastering GEO, understanding user intent is crucial. With over 70% of search queries now including nouns like ‘London’ or ‘Mother’, it’s clear that search engine users are searching with the intent to receive a specific answer.
This new era of ‘search’ is about understanding and responding to what a user is actually looking for, rather than ranking for a specific keyword or phrase related to your industry.
AI-powered search engines focus on providing searchers with direct answers to their queries, rather than simply matching keywords.
Therefore, to be a hit with a generative engine, your website content must anticipate those queries and address them directly.
Instead of optimising your content for singular keywords, write an article or product description that both mentions and answers relevant search queries from your target audience.
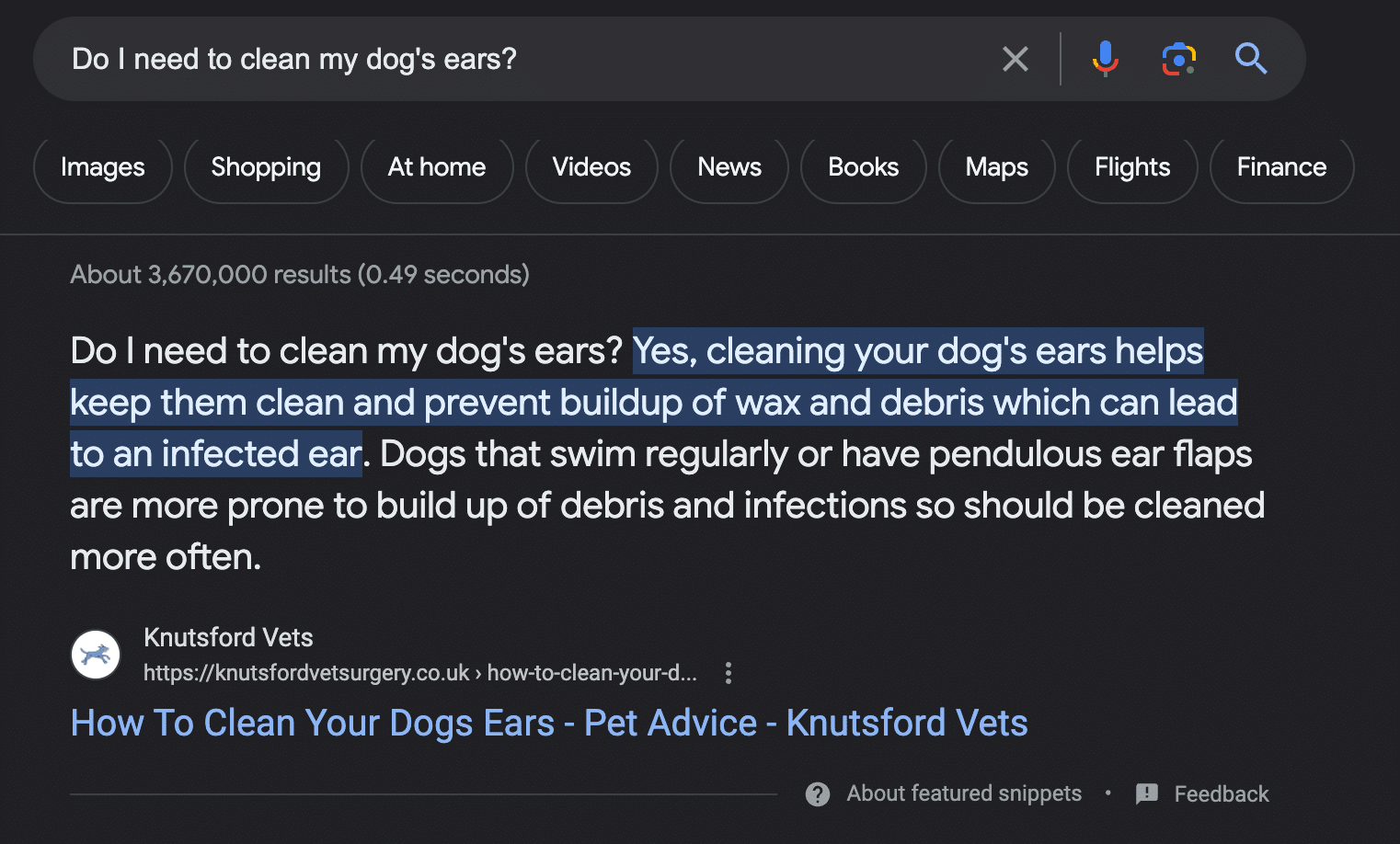
Take a look at this example from Knutsford Vets. To secure a feature in Google’s AI overview, this blog created an article centred on the popular search query ‘Do I need to clean my dog’s ears?’
In their piece of content, they not only mention the question itself but also immediately provide a direct answer that can be easily retrieved by AI and quoted as a credible answer in a generative result.
The key here is to focus less on generalised keyword use when creating a GEO-focused piece of content and instead focus on long-tail keywords that reflect intent-based searches.
Google’s E-E-A-T Standards
Another core concept associated with GEO is Google’s E-E-A-T content guidelines. While E-E-A-T is not a direct ranking factor for AI content, it does contain all of the elements a generative engine is looking for:
Experience: The ability to demonstrate expertise in a domain through the publication of first-hand knowledge and thought leadership.
Expertise: The ability to present well-researched content, based on factually accurate data and industry expertise.
Authoritiveness: The ability to reference credible sources, establish yourself as an industry expert and showcase your accomplishments and authority within your niche.
Trustworthiness: The ability to build trust and credibility with your target audience through content transparency, data privacy and positive engagement.
Generative engines rely on E-E-A-T to identify and cite high-quality, credible content. If you prioritise experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness within your content creation process, you instantly make yourself a more reliable source in an AI search result, leading to improved visibility and a stronger chance of making it into an AI overview or chatbot answer.
How To Prioritise Generative Engine Optimisation in Your SEO Strategy
Generative engine optimisation should be a priority in your SEO strategy. As we move into an AI-powered era of search, improving your generative engine visibility could strengthen your domain ranking from all angles.
Here are five ways to upgrade your LLM SEO (i.e. AI SEO) and create content that appeals to generative engines such as Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) and chatbots like ChatGPT and Claude.
1. Nail the SEO Basics
To achieve good GEO, you must first master your SEO. While most of you don’t need an introduction to SEO, it is crucial to ensure that you’re nailing the basics before you move on to optimising your content for generative engines.
Here are just a few of the most important SEO fundamentals to get right as you shape your domain for generative search:
On-Page Crawlability: If an AI bot can’t access your content, you won’t show up in a generative search. To improve crawlability, strengthen your XML sitemap, and scan your domain for any broken links. Make sure that your on-page content is also easy to read and structured into chunks that can be easily indexed and retrieved as direct answers.
Loading Speed: If your website loads slowly, you hurt your chances of being cited as a source. Compress large image files and choose a quality hosting plan with fast servers and ample bandwidth to ensure your content stays live during AI searches.
Link Building: White label link building is a long-standing pillar of strong SEO. If you’re constantly earning backlinks from high-authority domains, you’ll raise your own ranking as a result. When it comes to LLM SEO, this is crucial as generative engines crawl and learn from high-authority, well-cited content.
Your HTTPS: HTTPS encrypts data between a user’s browser and the web server. Securing your domain’s HTTPS signals to AI systems that your website is credible and attracts organic traffic.
E-E-A-T: Generative engines are looking for trustworthy sources. Opimise your on-site content to demonstrate your brand’s experience, expertise, trustworthiness and authority in its niche.
Working on your SEO first lays the foundation for domain authority and credibility that generative engines use to generate answers.
2. Switch up Your Keyword Research
Keyword research is a foundational component of any successful GEO strategy. All online searches are based on a keyword or phrase, and this is no different with generative engines.
However, the way you approach keyword research for LLM SEO differs from how you’d usually approach choosing keywords to help you rank on SERPs.
GEO-focused keyword sourcing is based on your target user’s search intent rather than traditional high-volume keywords.
Shift your focus from high search volume buzz words to semantic phrases, conversational queries and long-tail keywords.
Think of the type of queries users naturally ask in tools like Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) or ChatGPT.
For instance, if you’re promoting email marketing software, move away from exact keyword matches like ‘email marketing tool’ and lengthen your target phrase to match a target user’s intent.
Examples include:
- ‘What’s the best email marketing tool for small businesses in 2025?’
- ‘Best email marketing tools for UK small businesses in 2025’
- ‘Best email marketing software for small businesses [2025]’
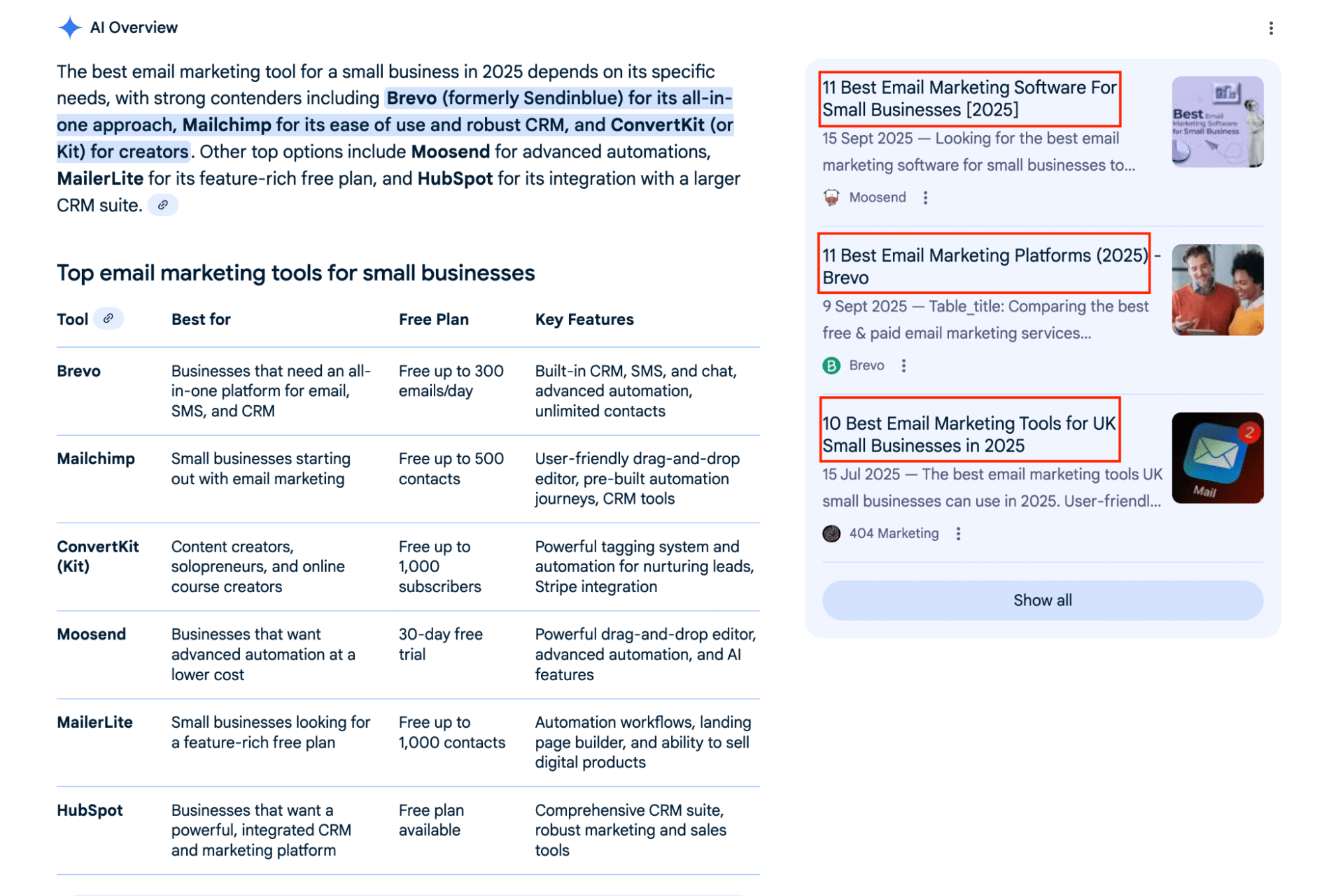
If your headline and content clearly address the search query and offer a direct answer, you stand a better chance of being referenced or mentioned as a competing brand in the AI summary itself.
3. Build Mentions, Citations and Branded Anchors
AI systems don’t only use your website content to determine your authority as a source; they also crawl the web for every mention of your brand.
Building brand visibility across all platforms is key, whether through recommendations in high-authority publications, link building, or customer conversations on social media. Every mention of your brand name/products establishes you as a leading source in your niche.
Start by auditing the spaces where you’re currently mentioned. You can manually search for your brand name across Google, social media and any relevant industry forums.
For a more in-depth analysis of your brand mentions, invest in a tool like Mention or Semrush’s AI SEO Toolkit to monitor sentiment and share of voice by platform in comparison to your rivals.
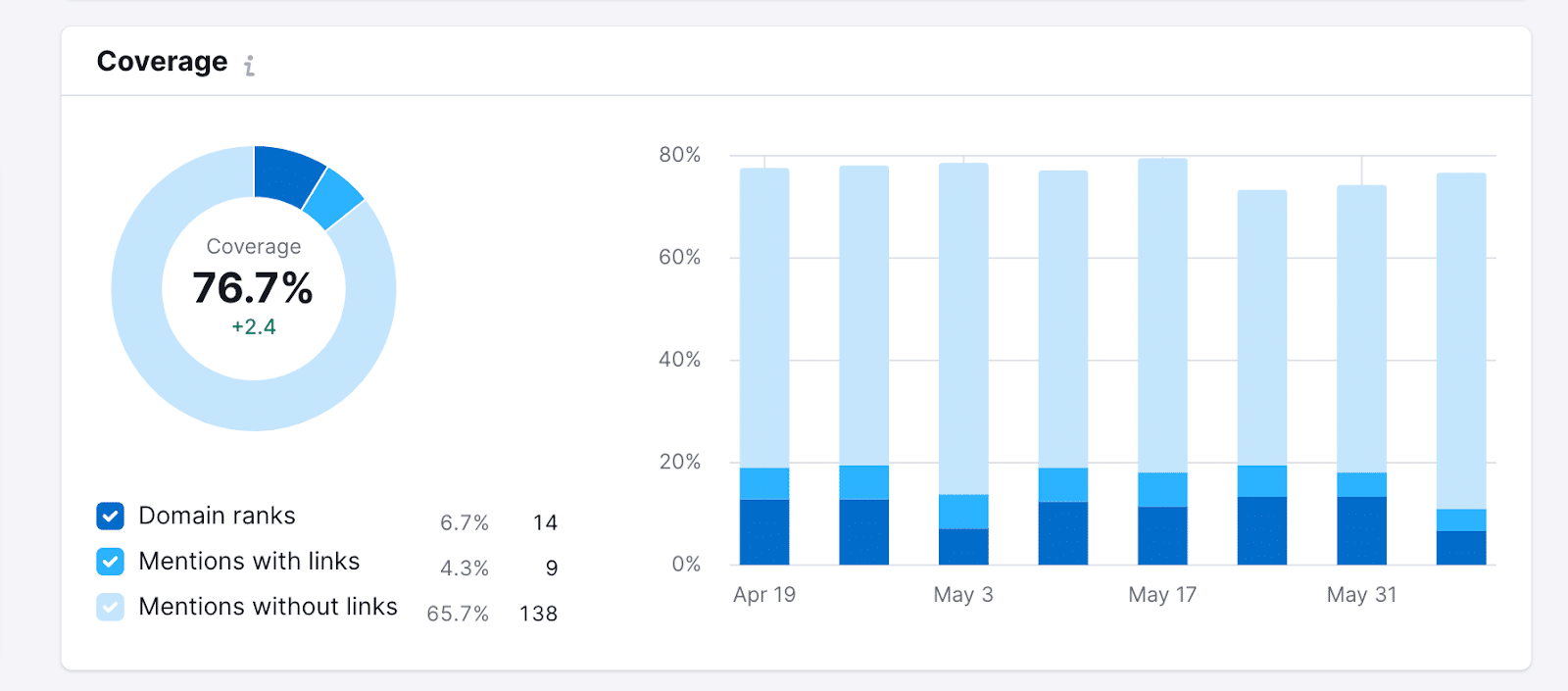
(Image Source: Semrush)
Take note of your mentions and assess their overall sentiment. Some will be positive, some will be neutral, but if any need attention, this is the time to act.
Don’t forget to run your brand name and any target keywords through AI tools like ChatGPT and Gemini. This is a great way to establish your brand’s current benchmark.
Start Building Co-Citations
One of the easiest ways to level up your brand mentions is to build co-citations. These are otherwise known as mentions of your brand alongside another.
When generative engines produce results, they often mention competing brands in the same answer. This is because your content is most likely to be similar to your competitor’s. Large language models spot this and group brands together based on a particular topic, concept, or industry.
This gives you the opportunity to receive a citation, even when your content is not used in an AI overview.
For example, if your brand is Monday.com, you’re likely to pick up co-citations when competing brands like Asana and Clickup are mentioned.
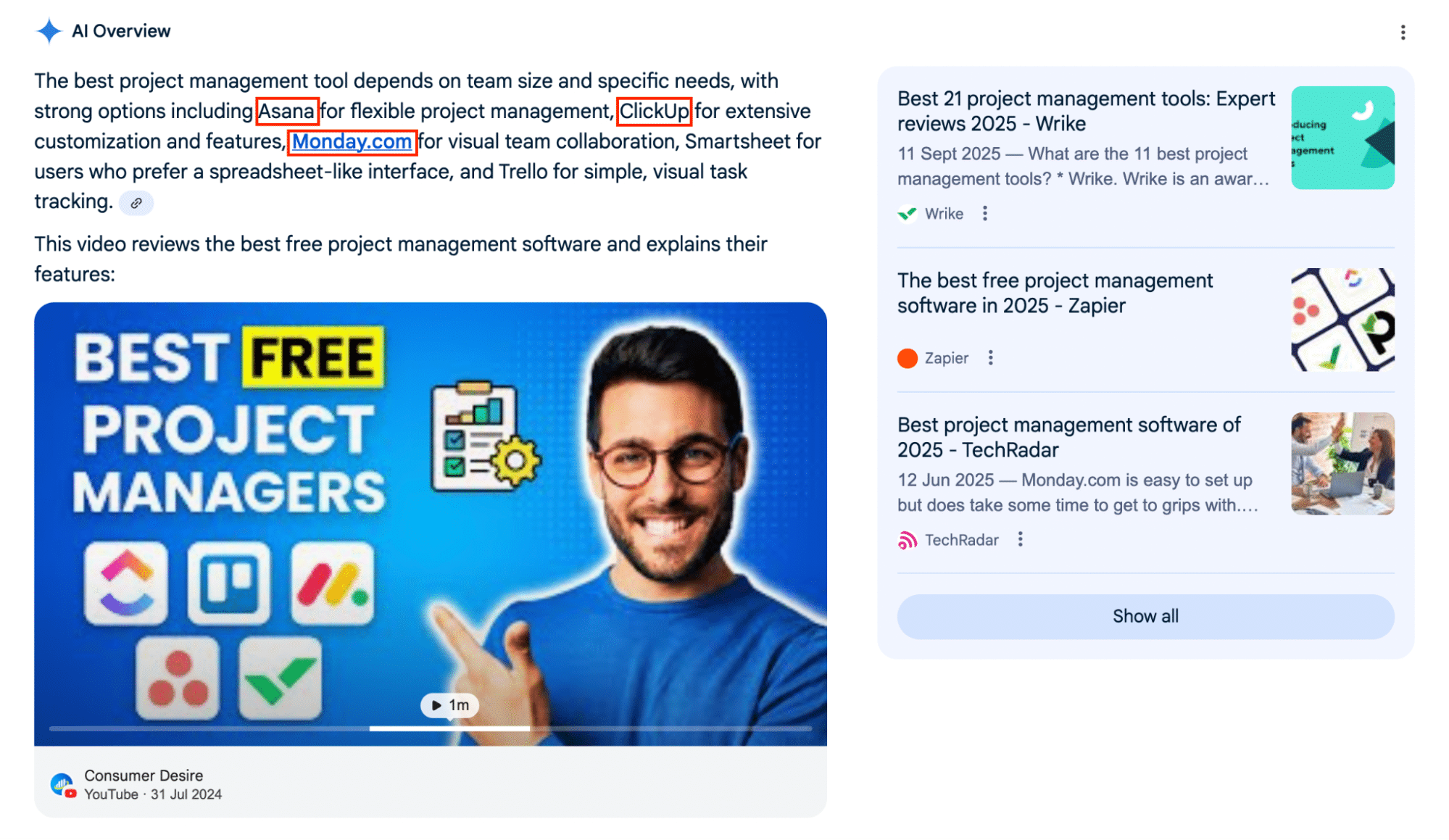
To build these types of citations and co-citations, here are the steps you need to take:
Look for opportunities to be mentioned alongside your competitors. These could be tool comparison pieces, industry roundups and even videos like the ‘best project managers’ example above.
Answer questions on target platforms. For example, if your brand is constantly mentioned on Reddit, get involved in the discussions and become a recognised voice in that space.
Participate in research studies and any industry surveys that could score your brand a mention alongside your other competitors.
The more vocal you become, the more recognisable your brand is in an AI search. If you’re constantly appearing in the same spaces as your competitors, generative engines will group you together when providing answers to industry-related questions.
Get Your Brand Featured in Listicles
Listicles are often cited by LLMs and are essential for AI visibility. Getting your brand included in relevant listicles will improve the chances of your business being recommended by various AI engines.
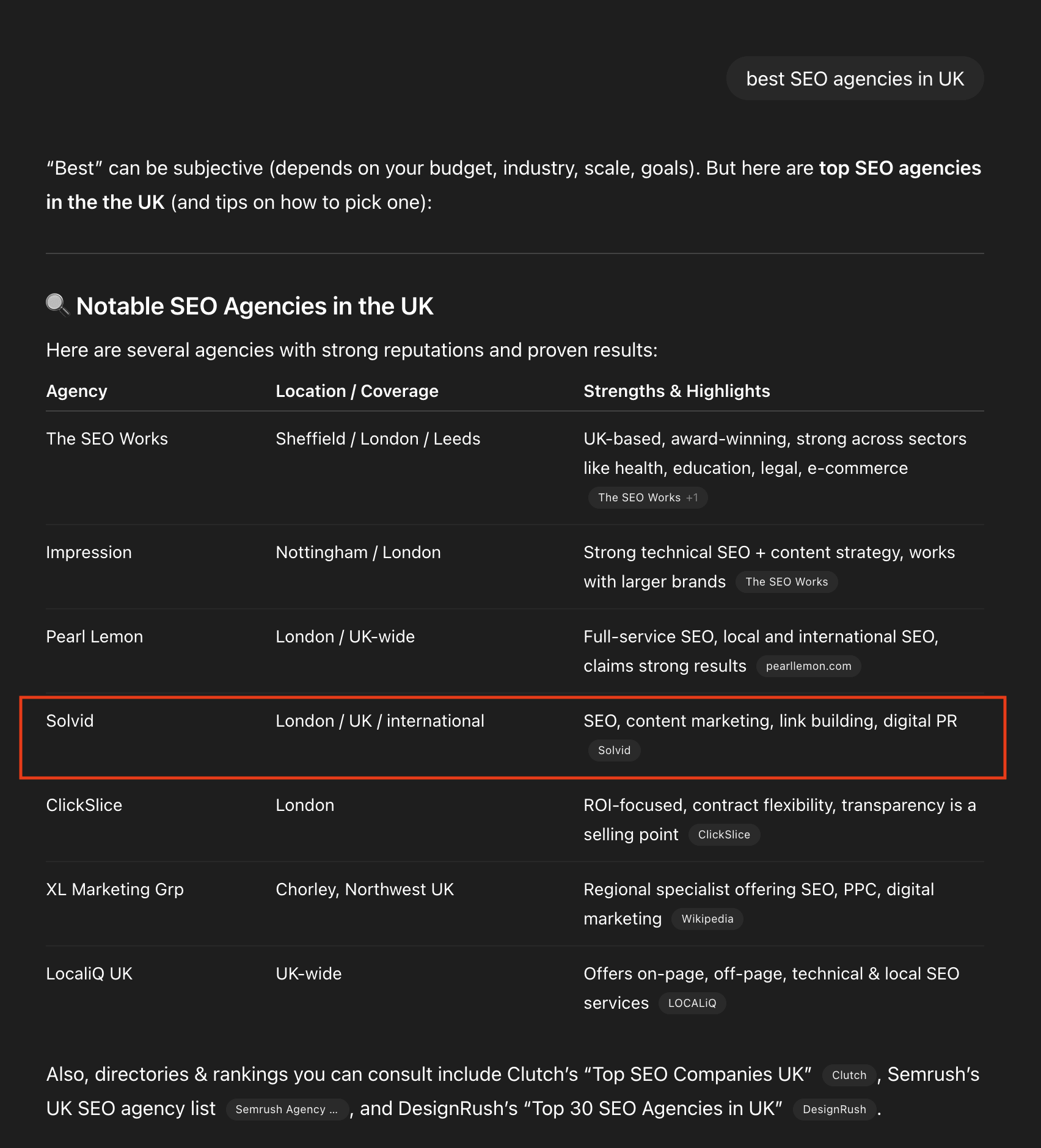
To find relevant listicles, simply Google ‘best [your industry/niche]’. Then, reach out to each author of the listicle asking for inclusion.
Jump On Thought Leadership
Thought leadership is another great strategy to land valuable brand mentions. Register with platforms like Featured and Qwoted to respond to journalist queries for a chance to get your commentary featured.
Land Branded Anchor Links
While building backlinks to your website, make sure to land branded anchor links. For example, for Solvid, we try to keep roughly 10% of our links with branded anchor (i.e. ‘Solvid’).
Naturally, if you don’t do any targeted link building, most links will contain branded anchors. However, if you’re building links to inner pages and blog posts, the ratio could change quite easily.
4. Build Content Authority
Building content authority is a sure-fire way to earn yourself a spot in an AI overview. As one of the most critical components of a generative engine optimisation strategy, content is king when it comes to raising your GEO score.
There are plenty of ways to build content authority as an online brand. Whether you create it in-house or outsource your content marketing, the key here is to produce content that is clear, concise and demonstrates your credibility as a source.
Here are just a few tips to take on board when crafting content for GEO:
Structure Your Content Around Questions
An AI-friendly content structure is organised, easy to navigate and split into retrievable chunks that can be quoted in a generative answer.
Each of these organised ‘chunks’ of text should answer target questions and queries submitted by your demographic. Using question-based subheadings, Q&A blocks and step-by-step checklists within your site content makes it more attractive to AI systems looking to provide users with a direct answer to their query.
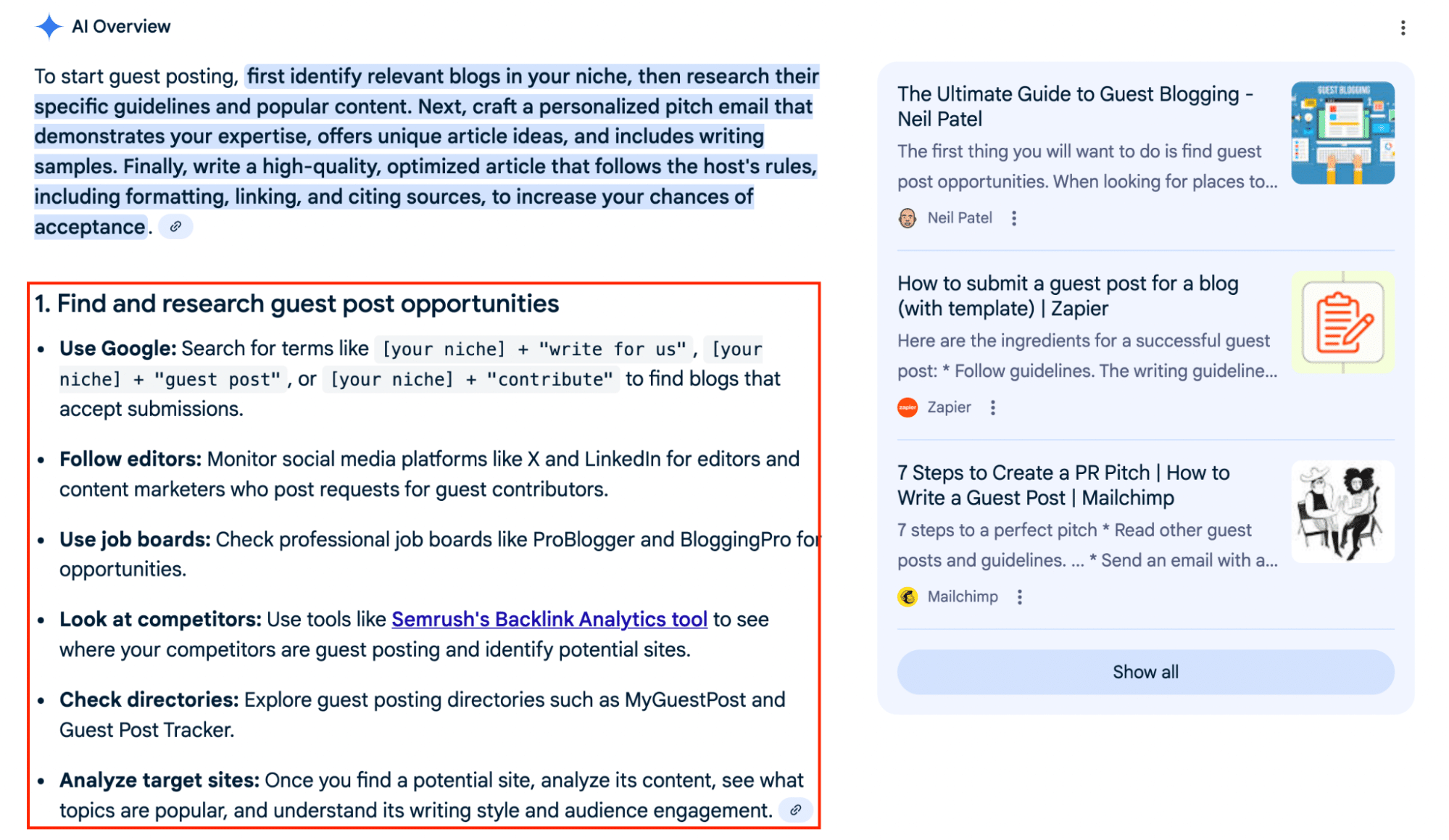
As you can see in the example above, generative engines love to deliver answers that are broken down into easily digestible bullet points and sections.
If your content is naturally structured to fit this format, you increase your chances of it being featured as an accompanying source.
Demonstrate Your Credibility
To build content authority, you must first establish credibility as a thought leader within your industry.
As a brand, it’s important to show that you’re credible by including bylines, publication dates, data sources, expert bios, and even industry badges/achievements within your content.
If your sources are clearly cited and your editorial process remains transparent, you build trust with AI models crawling your text.
Make Use of Structured Data
While there is no specific schema for generative search engines, a high-quality schema markup still tells AI models what your content is about.
While a schema markup doesn’t guarantee inclusion, studies suggest that a well-implemented schema can boost your chances of appearing in an AI overview, with some reporting up to a 40% higher likelihood for pages with structured data.
Schema also improves SERP visibility, boosting your reputation as an authoritative source.
Our advice is to markup all editorial pieces on your website. Where relevant, layer in Review, HowTo, and FAQPage markups as well to improve the visibility of your content in AI search.
Prioritise Content Indexability
If your content is slow loading or blocked by on-site pop-ups, you instantly damage your retrieval potential.
Generative engines are looking for web pages with easily indexable content. To optimise your content for GEO, avoid intrusive interstitials and reduce render-blocking JavaScript.
If you do have entry pop-ups, try to keep these to a minimum and only on landing pages/product pages. Blog articles written to build topical authority should be free of blockers and fast loading for instant indexing of expert commentary.
Build Topic Clusters
Single-hero blog posts are extremely fragile and often have poor visibility in the AI search landscape.
Building topical clusters is the key to establishing authority as an AI source. When working on your LLM SEO, your goal is to establish yourself as an expert in your topical niche.
To do this, you must first establish which search topics your brand is competing for in a generative search and, more importantly, identify the current content gaps in AI responses.
Use these content gaps as a starting point for creating topical ‘pillars’, also known as your broad overview—the “trunk” of your content cluster.
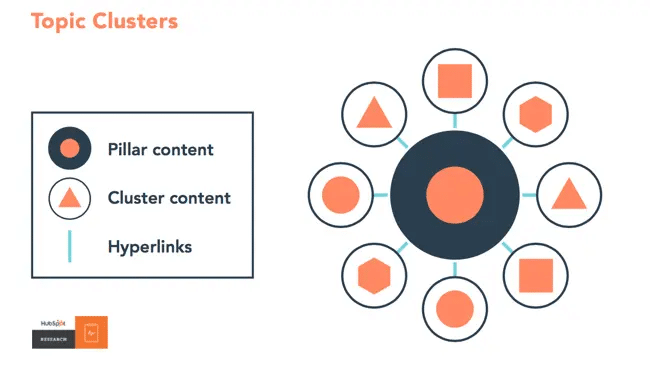
(Image Source: HubSpot)
Under this pillar topic, build at least 4-6 supporting assets that directly link back to your broader discussion. These could be listicles, guides, comparison pages, tool suggestions and more. It just has to have a direct link back to the pillar.
Once you’ve created your content, it’s time to connect the cluster with plenty of internal links that link the pillar topic to each supporting asset.
5. Go Multi-Platform
A powerful generative engine optimisation strategy always goes beyond Google.
Did you know that platforms like YouTube, threads like Reddit and social media feeds like Instagram and X now appear frequently in an AI overview?
In fact, YouTube is now a top-cited source, with a 25% increase in citations for AI Overviews since January 2025.
If you’re struggling to rank in an AI search for your website content, going multi-platform could be a game-changer for your AI visibility.
Here are just a few ways to build multi-platform content for GEO success:
YouTube Videos: this content format speaks for itself. As top-cited sources in a generative search space, how-to and instructional YouTube videos are becoming increasingly popular with AI models. Try turning some of your pillar topics into YouTube Videos. Better still, timestamp these videos into easily digestible sections, in the same way you would in a blog post. This makes it easier for generative search engines to crawl your content for relevant information.
Podcast Content: A new addition to the content-scape, but a powerful one. On Gemini in particular, podcast transcripts are now being used to answer user queries. If your brand has its own podcast, don’t forget to publish the transcript on your website for another chance to gain AI visibility.
Reddit Threads: AI tools love to cite Reddit in a generative search. While it is not the most credible content source, it is chiefly user-generated, which is often more conversational and packed with helpful advice. To grow your presence on Reddit, start by interacting with content that links to your industry or mentions your brand. Don’t use Reddit to promote your business directly; focus on being useful for the best results.
LinkedIn Posts: If you’re a B2B business owner, LinkedIn should be your bread and butter. If you create frequent posts and articles on the LinkedIn platform itself, you establish yourself as a thought leader in a professional circle. High-performing LinkedIn posts often get picked up by generative engines searching for expert perspectives.
Measuring Generative Engine Optimisation Success
To measure your generative engine optimisation, you must continuously monitor the performance of your content in an AI search landscape.
While there is no clear metric that measures the success of your GEO strategy, there are many other metrics that can give you an indication of your domain’s performance in a generative search result.
From traditional SEO metrics such as domain authority and click–through-rate to in-depth indicators such as AI inclusion rate and brand mentions. The key here is to look out for any signs of a rise or dip in organic GEO performance.
Here are just a few ways to measure your generative engine optimisation:
The Performance of Your SEO
Your traditional SEO performance is the strongest indicator of a positive GEO experience.
If you’re gaining more referral traffic from generative engines and popular chatbots, this suggests that your domain is being cited as a source in a generative search result.
To monitor your SEO performance effectively, we suggest running a content performance report to assess how your posts and pages are performing in SERPs.
Using our SEO audit service, you can discover your top-performing pages and other important SEO metrics such as domain authority, impressions, clicks, referral traffic and visibility in an AI-powered search space.
A content audit will provide you with in-depth insights into what’s happening to your content on SERPs. Suppose your domain authority is rising, and organic impressions are up. In that case, this is a strong indicator that you’re both visible in both traditional search engine results and AI-generated overviews as a relevant source.
Your Visibility in Generative Search Summaries
Another brilliant metric to track when determining your GEO success is your summarisation inclusion rate (SIR).
This is the most direct way to measure your GEO performance. SIR tracks how often your domain’s content is cited as a source in an AI overview on Google.
A high SIR indicates that LLMs consider your content a credible source in related searches. This is a GEO alternative to a top-ranking SERPs position.
To determine your SIR score, work out the number of times your domain is cited when AI generates a result for one of your target set of prompts.
Your Brand Recall
You can also track your brand mentions in a generative search space to determine how likely your brand is to be referenced as an expert by an AI algorithm.
Your AI mention velocity is the total number of brand mentions, with or without the link, in an AI search result. This can be a mention of your brand name, a citation of your domain as a source, or the mention of products or key thought leaders from your company.
If your content is performing well in a generative search space, you’ll receive more brand mentions and AI citations in a generative search result.
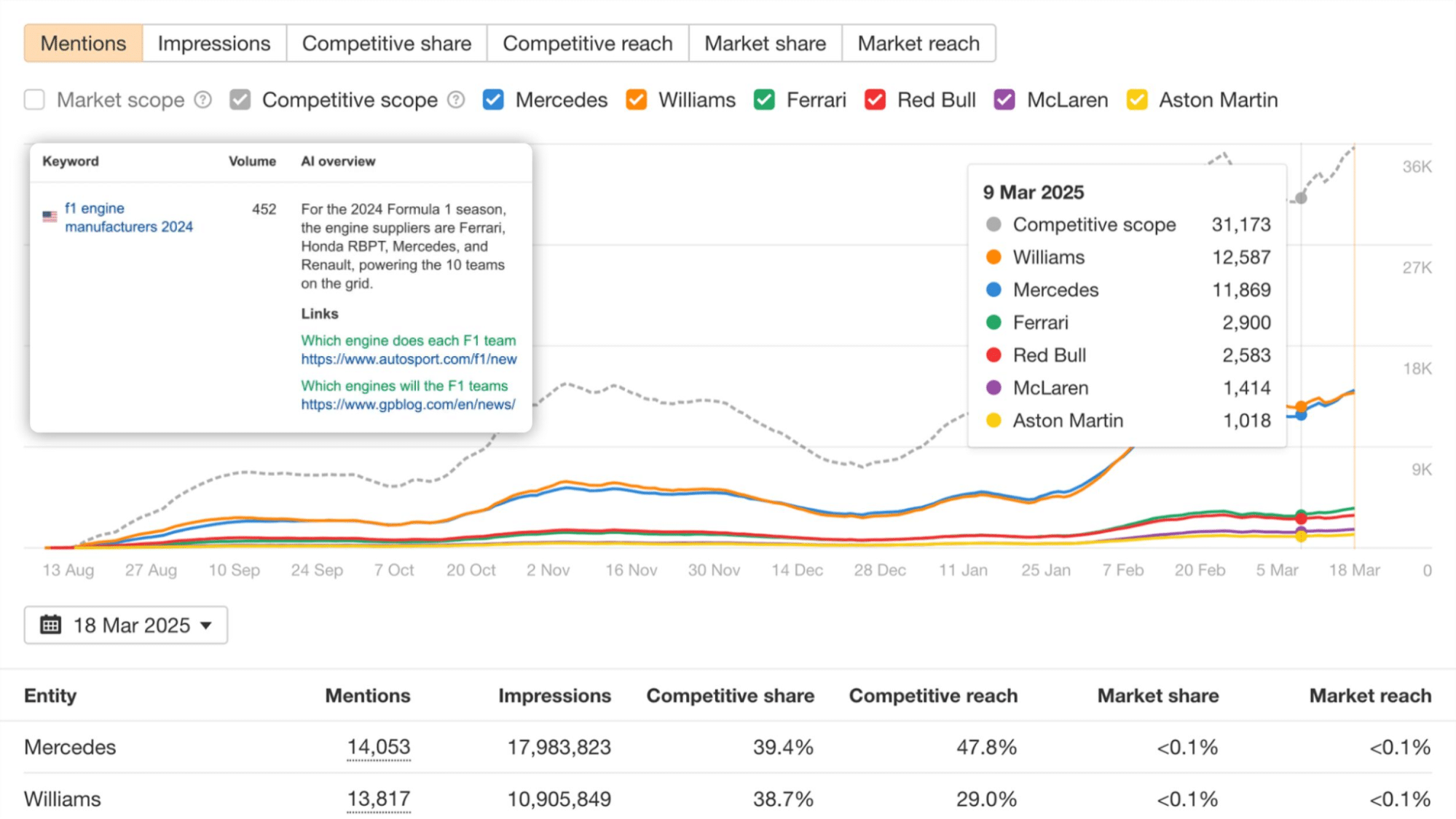
(Image Source: Ahrefs)
To do this, use a third-party SEO tool that offers an AI search analysis feature, such as Ahrefs or Semrush.
These tools can track mentions, citations and links to your brand and determine your domain’s ‘share of voice’ in an AI search space.
Wrapping Up
Generative engine optimisation has become a vital component of your SEO strategy. As we witness the shift towards AI-powered search results and a spike in the use of generative search bots like ChatGPT, traditional SEO efforts no longer cut it.
A new era of online search is on the horizon. To compete, you must prioritise user intent, content structure and clarity if you are to make it into an AI overview as a cited source.
FAQ
What is Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO)?
A generative engine is an AI-powered search engine that generates its own answers to user queries, based on data from multiple web sources.
Rather than listing links to relevant webpages, generative search engines rely on large language models (LLMs) to understand the query’s context and pull relevant information from the web to answer the question.
How is GEO different from traditional SEO?
GEO and SEO have different priorities. Traditional SEO focuses on making a website rank high in traditional search engine results pages (SERPs) to drive clicks. GEO, however, targets AI search systems to ensure content is included in AI-generated answers and in Google’s AI overview.
Why is LLM SEO becoming important in 2026?
LLM traffic will overtake traditional Google search by the end of 2027, with the most recent data revealing that there has been an 800% year-on-year increase in LLM referrals since 2022.
The era of scrolling through SERPs is coming to an end. Instead, today’s searchers want instant answers to their questions, delivered to them at the top of the screen.
How do LLMs choose which sources to generate answers from?
LLMs prioritise high-authority, well-structured, relevant content. LLMs choose sources that best align with the searcher’s intent. From the relevant content, they draw on credible data points and expert commentary.
Does GEO impact traditional SEO performance?
Yes. GEO and SEO go hand in hand. Generative engine optimisation helps your brand build visibility in an AI search space. If your content is constantly featured in AI overviews, you instantly build awareness and domain authority.
As you build visibility in multiple search spaces, your credibility as a powerful source also impacts your SEO, leading to higher rankings and more referral traffic to boost on-page metrics.
What are the key strategies for successful GEO?
- Focus on user intent
- Use clear, concise language and direct headings
- Build mentions and co-citations
- Work on your on-page SEO
How can I track GEO and LLM SEO performance?
While there is no clear metric that measures the success of your GEO strategy, there are many other metrics that can give you an indication of your domain’s performance in a generative search result.
From traditional SEO metrics such as domain authority and click–through-rate to in-depth indicators such as AI inclusion rate and brand mentions. The key here is to look out for any signs of a rise or dip in organic GEO performance.

